How To Build Financial Software: The Ultimate 2026 Guide

Financial software plays a critical role in how businesses and individuals manage, analyze and secure their financial activities. As fintech continues to evolve, understanding how to build financial software in 2026 requires more than just technical skills-it demands strategic planning, regulatory awareness and a security-first mindset. This ultimate guide walks you through the essential concepts, development steps, costs and best practices needed to create scalable and reliable financial software solutions in today’s digital economy.
What Is Financial Software?
Financial software, also known as financial system software, refers to a category of digital solutions designed to manage, automate and optimize financial activities for individuals, businesses and organizations. These systems handle a wide range of monetary functions, including accounting, payments, budgeting, financial reporting, forecasting and compliance management.
By automating repetitive financial processes and enabling secure transactions, financial software improves operational efficiency, accuracy and transparency. Users can track income and expenses, monitor cash flow, manage assets and liabilities and generate real-time financial reports to support data-driven decision-making.
Who Needs Financial Software?
Financial software is no longer limited to banks or large enterprises. It serves a wide range of users across industries, each with different financial management needs.
Individuals and households use it to track expenses, manage budgets and plan savings. Small businesses and freelancers rely on financial software for invoicing, payroll, tax management and cash flow tracking, helping reduce manual work and ensure compliance.
Large enterprises adopt advanced systems for financial reporting, forecasting, risk management and strategic planning, often through ERP and financial analytics platforms. Banks, financial institutions and fintech startups depend on secure financial software to power payments, lending and customer management, including CRM solutions for financial advisors.
Non-profit organizations and public institutions also use financial software to improve transparency through efficient fund tracking and reporting. Ultimately, anyone who manages or transacts money can benefit from financial software, making it essential in today’s digital economy.
Why Is Financial Application Development Important?
Financial application development plays a vital role in helping individuals and organizations manage complex financial operations efficiently and securely
- Solving Complex Financial Problems. Financial applications automate repetitive tasks, reduce human errors and simplify complex processes such as transaction management, reporting and forecasting. This enables faster decision-making and improves operational efficiency.
- Target Audience & Customization. Financial software serves diverse user groups, including individuals, SMEs, enterprises and financial institutions. Customizable features allow applications to meet specific user needs, ensuring better usability and higher adoption rates.
- Development Process & Compliance. Building financial applications requires careful planning, secure architecture, rigorous testing and continuous maintenance. Compliance with financial regulations, data protection laws and industry standards is essential to protect sensitive information and maintain user trust.
- Business Benefits. Well-designed financial applications enhance productivity, accuracy and security. They improve customer experience, support data-driven decisions and help businesses scale operations while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Types of Financial Software
The financial software landscape offers a wide range of solutions for both businesses and individuals. While many options exist, only certain types achieve widespread adoption and high user demand. Below is an overview of the most popular financial software categories, recognized for their strong market traction and practical value.
1. Accounting Systems
Accounting software plays a central role in managing financial operations efficiently. These systems come in multiple forms, each designed to support specific business needs.
- General Accounting Software records and processes financial transactions such as invoices, payments and expenses, generating detailed reports to assess financial performance.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software integrates financial management with other business functions, including human resources and inventory, providing a centralized platform for operational efficiency and strategic decision-making.
- Payroll Software automates salary calculations, tracks employee work hours and ensures compliance with tax regulations, with platforms like ADP serving as well-known examples.
- Billing and Invoicing Software streamlines accounts payable and receivable by automating workflows and reducing manual data entry errors.
- Inventory Management Software helps businesses track stock levels, manage orders and optimize supply chains, ultimately reducing costs and improving financial control.
Together, these accounting solutions support organizations of all sizes by improving accuracy, transparency and operational efficiency.
2. Payment Gateway Software
Payment gateways act as essential intermediaries in online transactions, enabling secure payments via credit and debit cards. They connect merchants and customers by verifying card details, confirming available funds and securely transferring transaction data between financial institutions.
Modern payment gateways integrate seamlessly with e-commerce platforms and financial systems, demonstrating high flexibility and scalability. With the global payment gateway market reaching $32.52 billion in 2023 and growing at an annual rate of 22.2%, these solutions continue to play a critical role in the expansion of digital commerce.
Financial software development companies such as Savvycom contribute to this growth by delivering secure, scalable payment solutions that adapt to evolving online business models. The rapid shift toward digital transactions has further reinforced the importance of payment gateways within the fintech ecosystem.
3. Insurance Software (InsurTech)
Insurance technology, or InsurTech, is one of the fastest-growing areas within financial software, with a projected CAGR of 34.4% and an expected market value of $1.19 billion by 2027. This segment is being transformed by data-driven innovation, particularly through the use of wearables and connected devices.

Modern InsurTech platforms leverage real-time data to offer personalized insurance plans, dynamic pricing models and tailored recommendations. Notably, smaller insurance providers are adopting these technologies to explore niche markets, lower customer acquisition costs and enhance competitiveness against larger insurers.
4. P2P Lending Platforms
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms represent a major shift in how borrowing and lending are conducted. By directly connecting borrowers with investors through digital marketplaces, these platforms remove traditional financial intermediaries.
P2P lending software emphasizes cost efficiency, transparency and accessibility, often offering more attractive terms than conventional banks. According to Webisoft, the global P2P lending market is projected to reach $558.91 billion by 2027, growing at a rate of 29.7%. As adoption increases, P2P platforms continue to reshape lending practices and promote decentralized financial services.
Financial Software Development Cost in 2026
The cost of developing financial software in 2026 varies significantly depending on business goals, system complexity and technology choices. From basic accounting tools to enterprise-grade fintech platforms, understanding cost components and estimation methods helps organizations plan realistic budgets and avoid unexpected expenses.
Key Cost Factors
Several critical factors directly influence financial software development costs:
- Project Scope & Complexity: Feature depth, integrations and system architecture greatly impact development time and cost.
- Technology Stack: Choices such as cloud infrastructure, blockchain, AI, or third-party APIs affect both initial and long-term expenses.
- Security & Compliance Requirements: Regulatory standards, encryption and security audits add essential but necessary costs.
- Development Team & Location: Team size, expertise and geographic location influence hourly rates and overall budget.
- Maintenance & Scalability: Ongoing updates, performance optimization and future scaling should be considered from the start.
Cost Estimation Methods
Accurate cost estimation relies on structured evaluation techniques:
- Bottom-Up Estimation: Breaking the project into smaller components and estimating costs for each feature or module.
- Analogous Estimation: Comparing the project with similar past software developments to forecast expenses.
- Time & Material Model: Flexible pricing based on actual development hours and resources used.
- Fixed-Price Model: A predefined budget suitable for projects with clearly defined requirements.
Using multiple estimation approaches often provides the most reliable budget projections.
Average Development Cost Breakdown
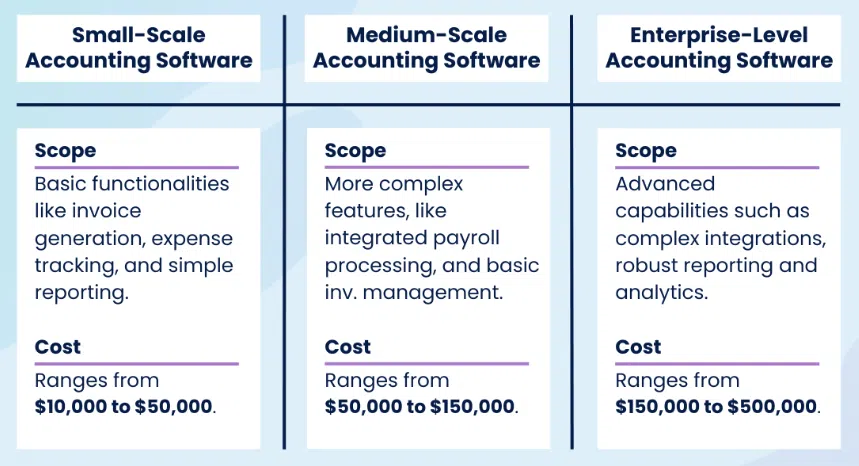
While exact costs vary, financial software projects generally fall into the following ranges:
- Small-Scale Financial Software: Basic accounting or budgeting tools typically cost between $10,000 and $50,000, depending on functionality and development time.
- Mid-Scale Solutions: Applications with integrations, analytics and enhanced security usually range from $50,000 to $150,000.
- Enterprise-Level Financial Systems: Large-scale platforms with complex workflows, regulatory compliance and scalability requirements often exceed $150,000, with costs increasing based on customization and long-term support needs.
Understanding these cost tiers helps businesses align development plans with their financial and strategic objectives.
How To Build Financial Software: Step-by-Step Guide
Building financial software requires a structured, security-first approach to ensure reliability, scalability and compliance. Below is a practical step-by-step guide:

- Define Project Requirements. Clearly identify the software’s purpose, target users and core functionalities such as transaction processing, reporting, or account management. Well-defined requirements reduce scope creep and improve development efficiency.
- Conduct Market Research. Analyze user needs, competitor solutions and industry trends to identify gaps and opportunities. Market research ensures the product aligns with real-world demand and regulatory expectations.
- Choose the Right Technology Stack. Select frameworks, databases and infrastructure based on scalability, performance and security needs. Common considerations include cloud platforms, APIs, blockchain and data encryption technologies.
- Design System Architecture. Create a scalable and modular architecture that supports future growth. Define data flows, system components and integration points to ensure flexibility and long-term maintainability.
- Develop Core Features. Focus on building essential features first, such as user authentication, account management and transaction handling. Prioritizing core functionality accelerates time-to-market.
- Implement Security & Compliance Measures. Apply strong security practices, including encryption, access control and regular security audits. Ensure compliance with financial regulations and data protection standards to protect sensitive information.
- Testing & Quality Assurance. Conduct comprehensive testing, including functional, performance and security testing. Quality assurance ensures the software operates reliably under real-world conditions.
- Deployment, Monitoring & Maintenance. Deploy the software in a controlled environment and continuously monitor performance. Regular updates, security patches and feature enhancements help maintain stability and meet evolving user needs.
Want to see AI in action across industries? Explore “AI in Finance, Healthcare & Retail: Driving Efficiency and Growth.”
Common Challenges in Financial Software Development
Developing financial software involves more than technical execution. Teams must address strict security, compliance and performance requirements while delivering a seamless user experience.
Security & Data Privacy
Financial applications handle highly sensitive data, making them prime targets for cyber threats. Implementing strong encryption, secure authentication and regular security audits is essential to protect user information and prevent breaches.
Regulatory Compliance
Financial software must comply with industry regulations and data protection laws that vary by region. Keeping up with changing compliance requirements adds complexity and requires careful planning throughout the development lifecycle.
Scalability & Performance
As user demand grows, financial systems must handle high transaction volumes without performance degradation. Designing scalable architectures and optimizing system performance are critical for long-term success.
User Trust & UX
Users expect financial software to be both secure and easy to use. Poor usability or unclear interfaces can erode trust, even if the system is technically sound. A balance between strong security and intuitive user experience is key.
Choosing the Right Financial Software Development Partner
Selecting the right development partner is a strategic decision that directly impacts project success. Icetea Software has proven experience in financial software development with deep expertise in security, compliance, and building scalable, future-ready solutions. With transparent communication, flexible engagement models, and long-term support beyond initial deployment, we help businesses transform fintech ideas into high-quality products.
Conclusion
Building financial software is a complex but valuable investment that enables efficient financial management, improved decision-making and sustainable business growth. From understanding requirements and development costs to addressing security, compliance and scalability challenges, a structured approach is essential. By working with the right development partner, businesses can successfully turn financial software ideas into secure, scalable and high-performing digital solutions.
————————————————————————
Icetea Software – Revolutionize Your Tech Journey!
Website: iceteasoftware.com
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/iceteasoftware/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/IceteaSoftware/
Twitter: https://x.com/Icetea_software






